Python单向链表
单向链表增、删、查、改操作 单向链表的使用,主要注意插入和删除这两项。
一、节点及链表定义
使用和操作链表,需要先定义节点。
节点至少包含两个变量:
- item:节点包含的数据内容
- next:节点指针指向
节点定义
class LinkNode: def __init__(self, val): self.item = val self.next = None链表定义
定义一个__head变量,指向链表的头部,初始化时,无元素,赋值None
class LinkList:
def __init__(self):
self.__head: LinkNode = None
二、链表遍历
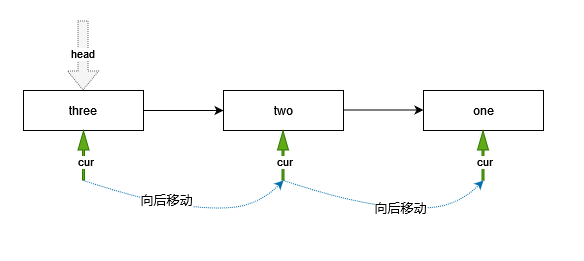
遍历即为访问链表的全部元素:
- 定一个cur变量为游标,从头部开始循环依次向后移动
- 直到节点为None时,说明尾部再无其他节点,到达链表尾部,循环终止
def travel(self):
cur = self.__head
while cur is not None:
print(cur.item, end='\t')
cur = cur.next
print()
三、链表查找
链表查找与遍历类似:
循环遍历整个链表,找到指定元素,返回True,
全部遍历完毕,未找到指定元素,返回False
def search(self, val):
cur = self.__head
while cur is not None:
if cur.item == val:
# print(cur.item,id(cur))
return True
cur = cur.next
print("Not found {}".format(val))
return False
四、链表插入节点
链表插入分为3种情况,头部,尾部以及中间插入
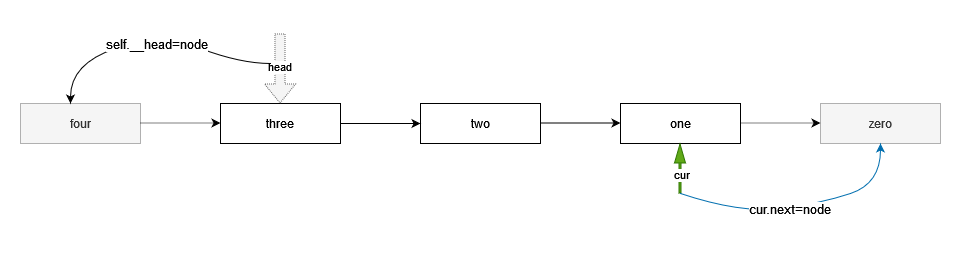
- 头部插入节点
- 新建一个节点;
- 新节点的指针指向链表的头部__head
- 将__head指向新节点
def addHead(self, val):
node = LinkNode(val)
node.next = self.__head
self.__head = node
- 尾部插入节点
- 首先判断链表是否为None,如为None即为空链表,则直接让__head指向新节点即可
- 游标cur遍历至最后一个节点;最后一个节点就是指针指向为None的节点
- 新建一个节点
- 将尾部节点指向新节点,即游标cur指向新节点
- 注意:这里的遍历方式(while循环)与遍历中的终止调节条件略有不同,因为需要用到游标cur,让游标指向新节点
def addtail(self, val):
node = LinkNode(val)
if self.__head is None:
self.__head = node
else:
cur: LinkNode = self.__head
while cur.next is not None:
cur = cur.next
cur.next = node
- 中间插入节点
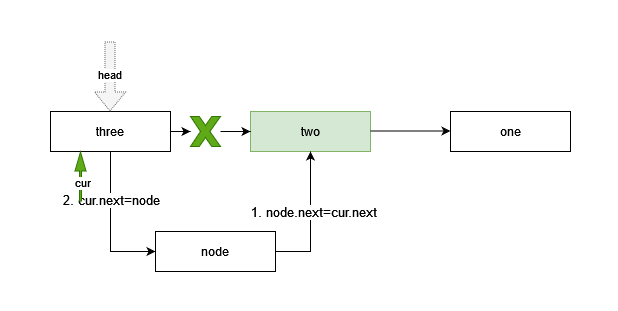
- 先判断插入位置pos与链表的长度,判断是在头部插入,还是在尾部插入;
- 根据指定位置插入新节点,同list操作,位置从0开始计算
- 首先需要将游标cur移动到指定位置pos的前一个元素,即pos-1处,这里使用count计数,需要小于pos-1
- 将新节点指向游标cur的下一个节点,即cur的next;
- 将游标cur指向新节点
- 中间插入注意2点:
- 游标cur需要指向位置pos的前一个节点;
- 注意插入节点指针链接的顺序,先将新节点指向下一个节点,然后将游标指向新节点
def insert(self, pos, val):
if pos <= 0:
self.addHead(val)
elif pos >= self.length():
self.addtail(val)
else:
cur = self.__head
count = 0
# 注意计数方式,count从0开始,即要即算到pos-1位置
while count < (pos - 1):
count += 1
cur = cur.next
node = LinkNode(val)
node.next = cur.next
cur.next = node
五、链表删除节点
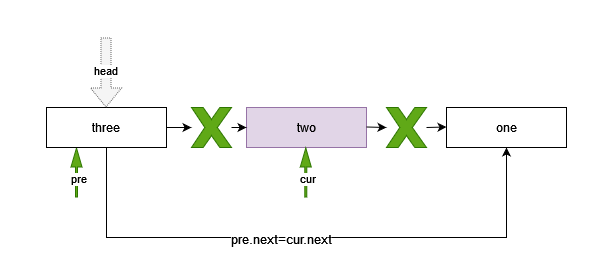
链表操作中,删除元素相对较复杂
- 定义两个游标变量:cur指向遍历的当前节点,pre指向上一个节点
- 遍历链表整个链表,游标cur和pre逐次向后移动,直到cur内容为删除的内容,或者cur遍历至最后一个节点
遍历过程:
如果找到指定元素,即游标cur指向的节点内容与删除内容相等
如果删除内容是链表的头节点__head是要删除的元素,则直接将__head指向下一个元素即可,
self.__head = cur.next如果要删除的内容不是头结点__head,此时,游标cur指向的是找到的节点,pre为前一个节点,则此时只需要将pre指向cur的下一个节点,
pre.next = cur.next如果遍历游标cur不是指定的内容,则将cur和pre继续向后移动,直到找到,或者链表全部遍历,
pre = cur cur = cur.next
def remove(self, val):
cur = self.__head
pre = None
while cur is not None:
if cur.item == val:
# 判断删除的元素是否为第一个元素(head)
if cur == self.__head:
print("find:{}".format(val))
self.__head = cur.next
else:
# 如果不是第一个元素,则将上一个元素指向下下个元素
pre.next = cur.next
return True
# 一个迭代,将pre指向当前元素,cur进入下一个元素
else:
pre = cur
cur = cur.next
return False
六、其他功能函数
- 判断链表为空
如果链表为空,则头部指针__head为None
def is_empty(self):
return self.__head is None
- 计算链表长度
同遍历功能,从头部开始计数
def length(self):
count = 0
cur = self.__head
while cur is not None:
cur = cur.next
count += 1
return count
七、完成代码
class LinkNode:
def __init__(self, val):
self.item = val
self.next = None
class LinkList:
def __init__(self):
self.__head: LinkNode = None
def addHead(self, val):
node = LinkNode(val)
node.next = self.__head
self.__head = node
# 注意,这里的while中与traval函数不同。next为None,表明无后续节点,已经遍历到最后一个节点
# travel函数则是判断node为None,表明本节点无数据,退出循环
# ==比较的是值,is not None比较的是地址
def addtail(self, val):
node = LinkNode(val)
if self.__head is None:
self.__head = node
else:
cur: LinkNode = self.__head
while cur.next is not None:
cur = cur.next
cur.next = node
def search(self, val):
cur = self.__head
while cur is not None:
if cur.item == val:
# print(cur.item,id(cur))
return True
cur = cur.next
print("Not found {}".format(val))
return False
def find(self, pos):
cur = self.__head
count = 0
if pos >= 0 and pos < self.length():
while count < pos:
cur = cur.next
count += 1
return cur.item
else:
return None
def remove(self, val):
cur = self.__head
pre = None
while cur is not None:
if cur.item == val:
# 判断删除的元素是否为第一个元素(head)
if cur == self.__head:
print("find:{}".format(val))
self.__head = cur.next
else:
# 如果不是第一个元素,则将上一个元素指向下下个元素
pre.next = cur.next
return True
# 一个迭代,将pre指向当前元素,cur进入下一个元素
else:
pre = cur
cur = cur.next
return False
def insert(self, pos, val):
if pos <= 0:
self.addHead(val)
elif pos >= self.length():
self.addtail(val)
else:
cur = self.__head
count = 0
# 注意计数方式,count从0开始,即要即算到pos-1位置
while count < (pos - 1):
count += 1
cur = cur.next
node = LinkNode(val)
node.next = cur.next
cur.next = node
def travel(self):
cur = self.__head
while cur is not None:
print(cur.item, end='\t')
cur = cur.next
print()
def length(self):
count = 0
cur = self.__head
while cur is not None:
cur = cur.next
count += 1
return count
def is_empty(self):
return self.__head is None